NeOpuntia® - Scientific

The healthy weight management lipophilic fibre
NeOpuntia® is a 100% natural ingredient made from dehydrated cactus leaves. Beyond its lipophilic properties (ability to interact with fats), NeOpuntia® also showed a positive effect on blood lipid parameters and Styndrome X diagnosis.
» Click and have a look at our website dedicated to Bio Serae's cactus ingredients
|
Applications |
|
|
Nature |
|
|
Active content |
|
|
Scientific Background |
|
|
Presentation |
|
Lipophilic properties
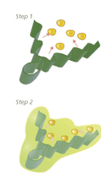
By lipophilic properties, we mean NeOpuntia®'s ability to attract and bind to fats when in their presence.
In more scientific terms, lipophilicity, or fat-liking, refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents. Lipophilic substances have a strong affinity with fats, which induces interactions between these lipophilic compounds and fats.
In vitro tests showed that the soluble and insoluble fibers contained in NeOpuntia® physically interacts with fats :
• Step 1 : Hydrophobic interaction takes place between fats & insoluble fibers
• Step 2 : Primary interactions are stabilized thanks to the soluble fibers (polysaccharides which create a fluid gel, stable at any pH).
NeOpuntia® can consequently be involved to reduce fat absorption into the body, with instant effect starting in the stomach.
The effect of NeOpuntia® on blood lipid parameters--risk factors for the metabolic syndrome (syndrome X).
Linarès E, Thimonier C, Degre M.
BIO SERAE Laboratories SA, Parc Technologique du Lauragais, Bram, France. e.linares@bioserae.com
Metabolic syndrome (syndrome X) causes millions of cardiovascular complications and premature deaths every year. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of NeOpuntia®, patented, dehydrated, Opuntia ficus-indica leaves, on blood lipid parameters and metabolic syndrome. Opuntia ficus-indica leaves are traditionally consumed as a vegetable. Participants in this monocentric, randomized, placebocontrolled, double-blind, 6-wk study were 68 women, ages 20 to 55 y, with metabolic syndrome and a body mass index between 25 and 40. Fifty-nine subjects completed the study according to the study plan. All volunteers followed wellbalanced diets with controlled lipid input. NeOpuntia® or placebo capsules were taken at a dosage of 1.6 g per meal. All 5 syndrome X criteria were measured on days 0, 14, and 42, including low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and triglyceride levels. For the 42 females above 45 y of age, we show a significant increase in HDL-C levels with NeOpuntia® and a tendency toward decreased triglyceride levels. At the same time, there was a decrease in HDL-C levels with placebo. Overall, for the entire study population, similar but less pronounced tendencies were demonstrated. Forty-two females taking NeOpuntia® with no additional hypolipemic treatment, had a pronounced reduction in LDL cholesterol, especially after day 14. At the study end, 39% of the NeOpuntia® group, but only 8% of the placebo group, were no longer diagnosed with metabolic syndrome. Our results indicate an advantage of using NeOpuntia® in dietary supplements and functional foods because of improvement of blood lipid parameters associated with cardiovascular
Effect of Opuntia ficus indica on symptoms of the alcohol hangover.
Wiese J, McPherson S, Odden MC, Shlipak MG.
General Internal Medicine Section and Department of Medicine, Tulane Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, LA, USA. jwiese@tulane.edu
BACKGROUND: The severity of the alcohol hangover may be related to inflammation induced by impurities in the alcohol beverage and byproducts of alcohol metabolism. An extract of the Opuntia ficus indica (OFI) plant diminishes the inflammatory response to stressful stimuli. METHODS: In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial, 64 healthy, young adult volunteers were randomly assigned to receive OFI (1600 IU) and identical placebo, given 5 hours before alcohol consumption. During 4 hours, subjects consumed up to 1.75 g of alcohol per kilogram of body weight. Hangover severity (9 symptoms) and overall well-being were assessed on a scale (0-6), and blood and urine samples were obtained the following morning. Two weeks later, the study protocol was repeated with OFI and placebo reversed. RESULTS: Fifty-five subjects completed both the OFI and placebo arms of the study. Three of the 9 symptoms-nausea, dry mouth, and anorexia-were significantly reduced by OFI (all P<.05). Overall, the symptom index was reduced by 2.7 points on average (95% confidence interval, -0.2 to 5.5; P =.07), and the risk of a severe hangover (>/=18 points) was reduced by half (odds ratio, 0.38; 95% confidence interval, 0.16-0.88; P =.02). C-reactive protein levels were strongly associated with hangover severity; the mean symptom index was 4.1 (95% confidence interval, 1.2-7.1; P =.007) higher in subjects with morning C-reactive protein levels greater than 1.0 mg/L. In addition, C-reactive protein levels were 40% higher after subjects consumed placebo compared with OFI. CONCLUSIONS: The symptoms of the alcohol hangover are largely due to the activation of inflammation. An extract of the OFI plant has a moderate effect on reducing hangover symptoms, apparently by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators.






